Decreasing cost of solar PV materials, its versatility, and global shift towards greater carbon neutrality contributed to its increasing popularity as a renewable energy source.
London, 15 March 2023 — Over 30% of utility-scale renewable projects globally between 2013 and 2023 were solar photovoltaic (PV) projects, according to a new report from the Energy Industries Council (EIC), the world’s leading energy trade association.
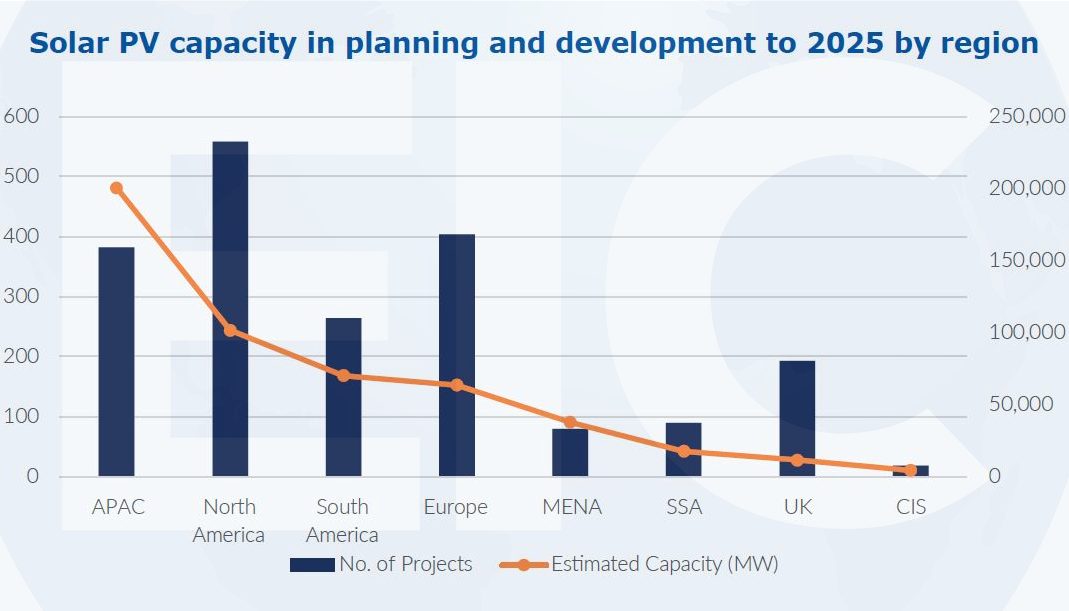
The EIC’s global solar insights report shows that current global utility-scale PV capacity is around 154 gigawatts.
The cost of solar is a key driver of investment in the industry, with the levelised cost of electricity of newly operational utility scale solar PV projects declining by 88% between 2010 and 2021 on a global average, according to the report.
The report’s data is sourced from the EIC’s proprietary EICDataStream and EICAssetMap global energy project databases.
Solar PV’s versatility has also contributed to its popularity, according to the report, as it can be installed on rooftops, floating, or ground-mounted, improving grid capacity with energy storage. Once its intermittency issues are solved through energy storage, solar PV can enhance grid capacity, especially in poorly connected areas.
“Renewable energy has become a key pillar of the global transition towards a more sustainable future,” said Neil Golding, Head of EIC’s Market Intelligence. “The growth of solar PV capacity is a testament to the increasing demand for clean energy solutions and it’s certainly a key component of the global ambitions to achieve our net-zero emissions targets.”
“China is still dominating the global solar PV supply chain, leaving regions like Europe heavily reliant on low-cost Chinese imports,” Rebecca Groundwater, EIC’s Head of External Affairs. “But Russia’s war on Ukraine coupled with forced labour concerns and logistics disruptions during Covid-19 highlighted the risks of relying on imports. In the US, the Inflation Reduction Act is expected to give domestic manufacturing a boost. As a result, we could see a real opportunity for first movers in the solar supply chain throughout Europe and the Americas.”
While some regions have been slower to adopt solar PV technology, major investments are being funnelled into the industry to ensure renewable energy goals can be achieved. According to EICDataStream, North America and Europe are leading in the number of projects.
The Biden administration aims to reach 40% electricity demand with solar power by 2035, and the Inflation Reduction Act provides tax credits and incentives for renewable energy adoption.
Spain is also a leading market for solar PV globally, contributing to the European Commission’s increased renewable energy target of 45% by 2030 as outlined in the REPowerEU Plan. The region is responding to the energy crisis as a result of Russia’s ongoing invasion of Ukraine.
The Asia Pacific region is at the forefront in terms of estimated capacity, with India alone having over 120GW of solar PV capacity planned or in development. India announced plans for 500GW of total non-fossil capacity and net-zero emissions by 2070 during COP26 in 2021.
Other APAC countries among the top ten global solar PV markets include Australia, which is pursuing green hydrogen ambitions, and Indonesia, which is aiming to develop solar PV to meet increasing electricity demand.
To view the full 104-page report, please visit the following link: https://www.the-eic.com/MediaCentre/Publications/Reports