PES presents an illuminating despatch from Fronius International GmbH that explores the challenges presented by Smart Grids and how these challenges can be met with integrated inverters.
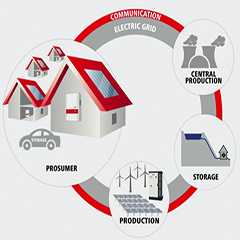
As the number of decentralised energy generators grows, also the need for an intelligent power grid rises. In the Smart Grid of the future, the parties of the energy system are not just connected via the electric grid but also via communication. The communicating parties are for example producers, consumer, storage, grid operation and trade.
The aim of such a Smart Grid is a stable and optimised power supply in a changing system. The most important issues are:
• Integration of Renewables: Smart
Grids enable the integration of a massively increasing amount of decentralised electricity producers
into the distribution grid
• Dynamic Control: Smart Grids are better controllable. They allow mechanism to stabilise the grid and increase security
of supply
• Grid Synergies: Smart Grids enable more efficient use of energy through optimising the local grid management and local energy balance at the customer
• Cost Optimisation: At long-term Smart Grids minimise the costs of the transition of the energy system and keep the electricity grid costs low
Smart Grids need a lot of intelligent (smart) devices and coordination between them. In this context, power production, especially PV due to its large share, plays a major role.
PV inverters are ready to be fully integrated in a Smart Grid. At the moment, they are among the smartest devices in the grid. There are three main reasons for this statement.
1) Advanced Grid Features
2) Communication
3) Future-proof