News
Solar PV and wind power market in the US will be driven by favorable government policies, says GlobalData
Published in: Solar, Press Releases
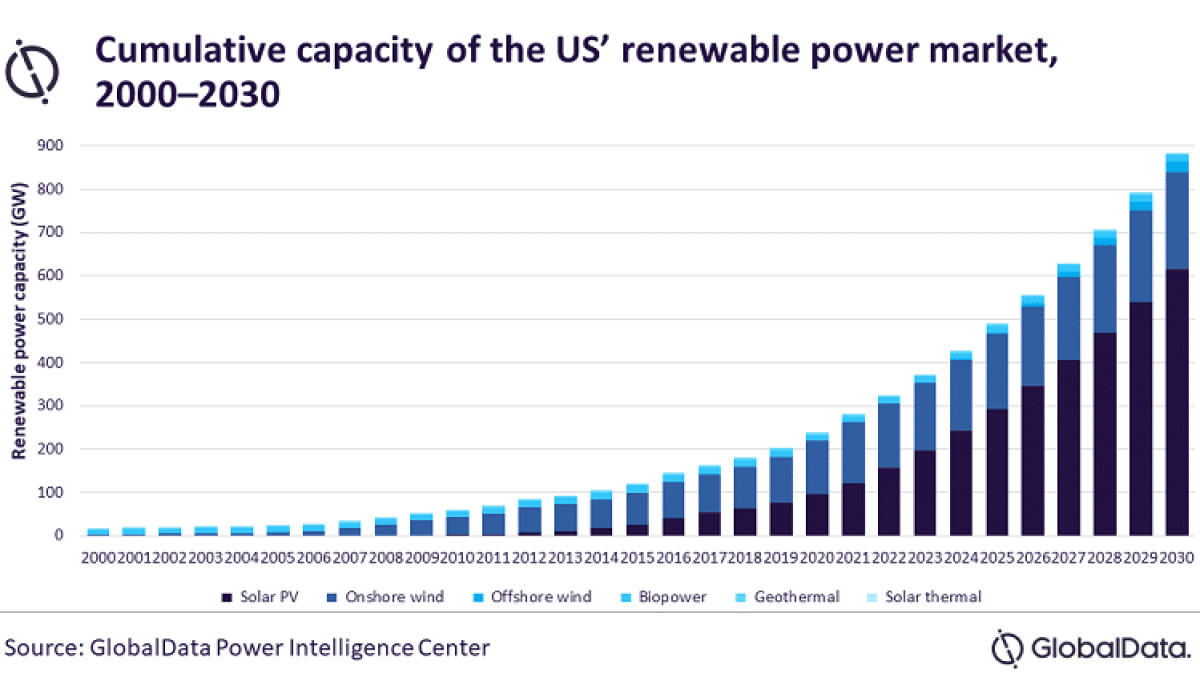
Renewable power held a 19% share of the US's total power capacity in 2020, according to GlobalData, and this share is expected to increase significantly to 48.4% by 2030. The leading data and analytics company notes that favorable policies introduced by the US government will continue to drive the country's renewable sector, particularly solar PV and wind power.
According to GlobalData's report, 'United States Power Market Outlook to 2030, Update 2021 - Market Trends, Regulations, and Competitive Landscape', installed renewable capacity* increased from 16.5 GW in 2000 to 239.2 GW in 2020, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.3%. By 2030, the cumulative renewable capacity is expected to rise to 884.6 GW, growing at a CAGR of 14% from 2020 to 2030. Despite an increase in prices of renewable equipment such as solar modules in 2021, the US renewable sector will show strong growth during the 2021 to 2030 period as this increase in equipment prices is short term due to supply chain disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Rohit Ravetkar, Power Analyst at GlobalData, says: "The expansion of renewable power capacity during the 2000-2020 period has been possible due to the introduction of federal schemes such as Production Tax Credits, Investment Tax Credits, and Manufacturing Tax Credits. These have massively aided renewable installations by bringing down the cost of renewable power generation and making it at par with power generated from conventional sources."
Over the last few years, the cost of solar PV and wind power installations has declined sharply. Since 2010, the cost of utility-scale solar PV projects decreased by around 82% while onshore wind installations decreased by around 39%. This has supported the rapid expansion of the renewable market. However, the price of solar equipment has risen due to an increase in raw material prices and supply shortages. This may slightly delay the financing of some solar projects that are already in the pipeline.
Ravetkar adds: "The US will continue to add significant renewable capacity additions during the forecast period to meet its target of reaching 80% clean energy by 2030. In November 2021, President Biden signed a $1 trillion Infrastructure Bill, within which $73 billion is designated to renewables. This includes not just renewable capacity building, but also strengthening the country's power grid and laying new high voltage transmission lines, both of which will be key to driving solar and wind power capacity additions."
*Excluding hydropower










-Feb-02-2026-07-32-32-1624-AM.jpg)
