• Noise mitigation by biomimicry of owl wing’s trailing edge fringe
• Product launch “Next Generation DinoTail”
• Serial production to be started soon
Silent operation of turbines is crucial for the success of many onshore wind projects. Siemens has therefore conducted extensive R&D over the last years to further reduce the noise of its wind turbines. An important breakthrough has now been achieved with the launch of a new generation of Siemens’ so-called DinoTail, an aerodynamic blade add-on. The trailing edge fringe of an owl’s wing provided the inspiration for this noise-reducing component.
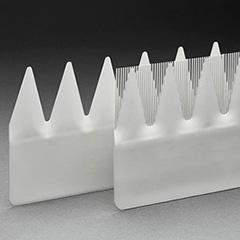
Owls are silent hunters. Flying without noise allows them to stealthily approach their prey – primarily smaller rodents. This is enabled by a particular structure of the owl’s wings: A serrated, fringed structure at the trailing edge, and small combs at the leading edge of the wings are believed to mitigate the noise of the air flow by generating fine vortices. This effect is now used by a new Siemens invention which optimizes the aeroacoustic performance of rotor blades.
In addition to vortex generators on the blade surface, Siemens now equips trailing edges with a combination of serrations and combs. This combed teeth concept creates fine vortices at the point where the fast air stream from above the blade profile meets the slower flow from below. As a result, the aerodynamic noise from the trailing edge of the blade is reduced significantly.