By now we are all familiar with the sight of wind turbines or solar panels and are aware of their part in the global energy transition. But there are many more sources of renewable energy available to us, some more surprising than others! In our latest article, the Institute has delved into some of the most innovative and unusual ways of generating renewable energy that you might not have heard about. Read on to find out more.
Wind Trees
Wind power is a crucial form of renewable energy, with new wind farm projects regularly being given the green light across the globe. But have you heard of wind trees? These are ‘micro-turbines’ that have been made to look more like trees than traditional bladed turbines. They are made up of a metal tree-like structure and numerous small turbines designed to look like leaves; they also have up to 4 batteries to store the energy they generate. These amazing structures could potentially provide enough power (approximately 18,000kwh per year) for a 4-person household in the right conditions.[1]

Renewable energy innovators hope that this may provide a way for renewable energy to be incorporated into private homes, or into urban spaces that have less free land available for wind farms. In some cases, they can also be incorporated with small solar photovoltaic components in order to collect both wind and solar power.
One company designing these trees is New World Wind, based in France. They have named their innovation, Aeroleaf.
As [Aeroleaf] is biomorphic, people cannot see at the first look that it is a renewable system… With our technology, we can provide energy seven days a week, 24 hours a day.”
Luc Eric Krief, New World Wind
Other benefits include their scale; as they are much smaller than turbines (no more than 10 metres tall), they can be installed without the need for extensive construction periods or engineering requirements. The wind trees are also very quiet, ensuring that they can be used in residential and urban environments without negative impact on humans or wildlife. New World Wind also claims that the wind tree is also fully recyclable at the end of its life.[2]
Unlike traditional turbines, wind trees are not connected to the national grid, but instead directly connect to a building’s electrical system, much like residential solar panels. They come with a high cost however, with an Aeroleaf WindTree costing over 50,000 euros, significantly more than traditional solar panels. However, as a relatively new technology, they may well reduce in cost in the future.
While they will never be the answer to the global energy transition on a large scale, they are nevertheless an interesting alternative for people wishing to increase the energy efficiency and decrease the carbon footprint of their homes or businesses.
Kinetic Tiles
Kinetic tiles capture energy from human movement and convert it into electricity. One widespread and innovative use of these tiles is in dancefloors, where kinetic energy is abundant.
Each kinetic tile contains a generator that is activated by movement, such as dancing, that generates power which is then stored in a supercapacitor. Each tile can then be linked up so that this energy can be used to power elements like lighting.[3]

This technology can also be incorporated into more ‘everyday’ scenarios as well, for example pedestrian pavements, as was seen in the UK in 2022. In this experiment, a small stretch of kinetic pavement was used to power nearby phone chargers, which not only created renewable energy but also engaged passers by in the importance of switching to sustainable energy sources.[4]
Researchers believe that these tiles could be used in schools and workplaces as well to power things such as Wi-Fi. [5]Manufacturers also claim that kinetic tiles can be made using recycled materials, including recycled plastic, therefore further reducing their environmental impact. [6]
In 2024, Coldplay announced that they had been able to reduce the overall carbon footprint of their world tour by 59% compared to their 2017 tour.[7] Kinetic dancefloors were just one small part of this endeavour but it seems we can expect to see more of this technology in the coming years, as we move towards a net zero future.
Suppliers of kinetic tiles are available across the globe, with innovators having worked on this technology since the early 2000s.[8] Why not consider kinetic tiles for your next event!?
Marine Life
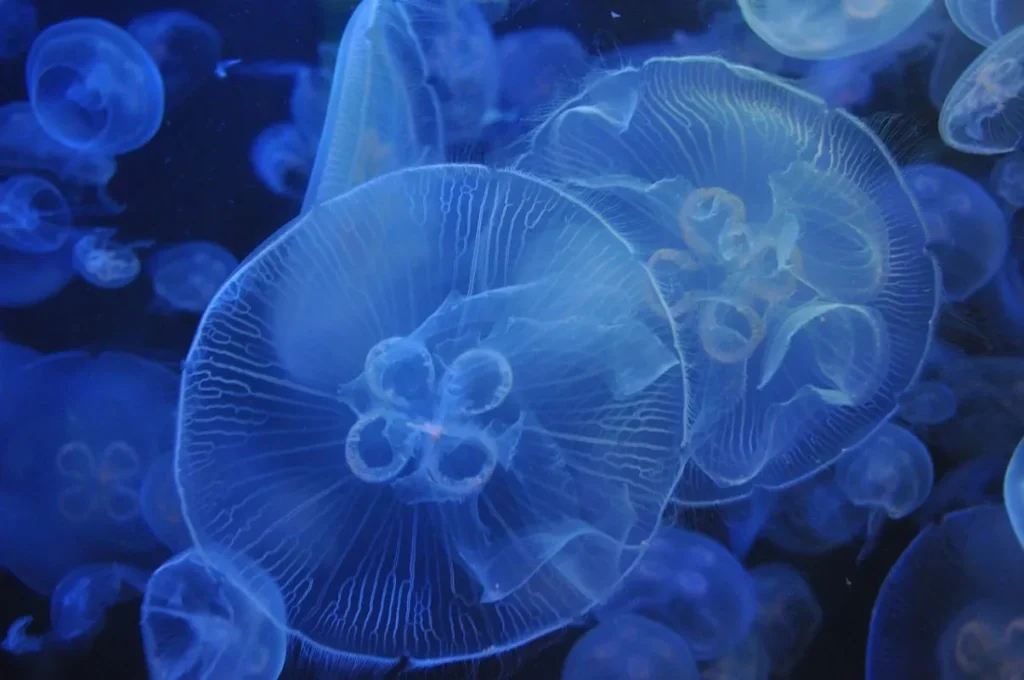
ellyfish contain a green fluorescent protein (GFP) which when placed under UV light can absorb photons and emit electrons.[9] As such, these proteins could be used in the solar panels of the future, replacing the use of silicon cells which are extremely energy intensive to manufacture and hard to recycle at the end of their life.
Experiments to test the viability of this have been underway since 2010 but have unfortunately stalled somewhat, with researchers focusing more on how GFP could be used as a sustainable replacement for LED lighting.[10]Nevertheless, with further research there is still potential for jellyfish proteins to be used to create cheaper and more efficient solar panels in the future.

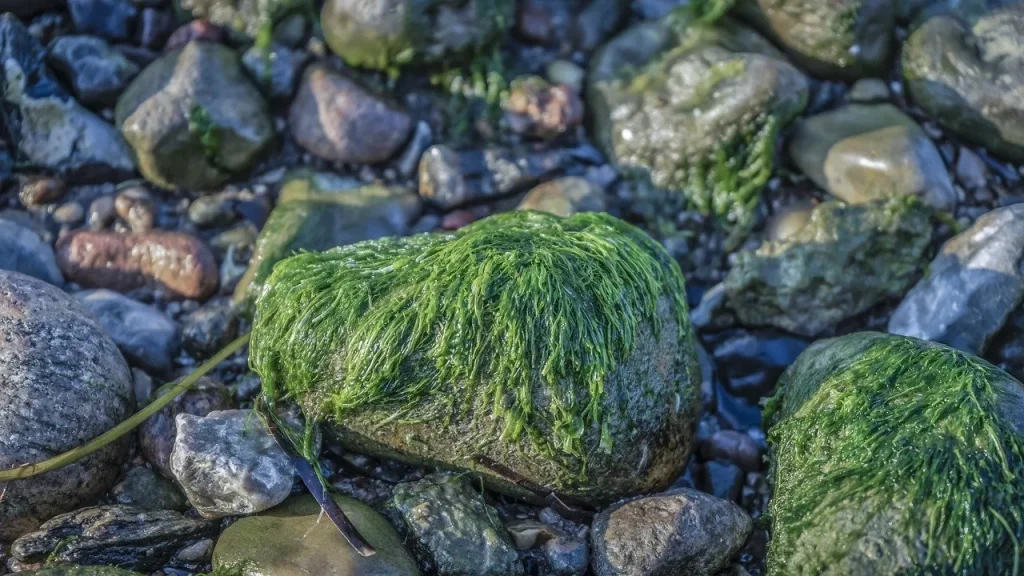
What’s more, jellyfish are not the only potential source of renewable energy that can be found in the sea! Scientists have also used algae to generate bio-photovoltaic energy, using the plant’s natural
photosynthesising process. Furthermore, photosynthesis also requires CO2 to take place, adding further benefits to this innovative practice by removing CO2 from the atmosphere and ensuring no further emissions are released.
The potential to use this energy in different sectors of society is wide-ranging. The Danish Technological Institute were even able to power a car for over 50 miles, using a biofuel made from seaweed and algae![11]

Conclusion
It’s clear that these unconventional renewable energy sources aren’t the magic answer to the global energy transition. However, they represent the unending research and innovation that is taking place across the globe in the field of renewable energy and energy efficiency. Without this, we cannot make a net zero future a reality.
While the REI doesn’t provide courses on jellyfish, you can increase your knowledge on the more conventional sources of renewable power, including solar, wind and hydrogen, via our wide range of accredited courses. Kick-start your career in renewable energy and you could be part of the next big breakthrough in sustainable energy!
[1] https://www.euronews.com/green/2023/11/12/could-wind-trees-with-micro-turbines-be-a-solution-to-green-energy-in-tight-urban-spaces
[3] https://powerhub.com/powering-the-dance-floor-with-electricity/
[4] https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-england-shropshire-63515244
[5] https://powerhub.com/powering-the-dance-floor-with-electricity/
[6] As above
[7] https://www.coldplay.com/emissions-update/
[8] https://www.forbes.com/sites/eamonnforde/2021/11/10/people-power-kinetic-dance-floors-to-power-clubs-and-concerts/
[9] https://oilprice.com/Alternative-Energy/Renewable-Energy/Another-Energy-Tech-Breakthrough-Involving-Jellyfish.html
[10] As above