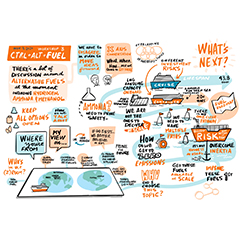
If LNG is a ‘bridge’ fuel, how long is the bridge? And, more importantly, where is it leading? Those questions framed discussions at a series of virtual workshops hosted by Gas Fest and Society for Gas as Marine Fuel (SGMF) last week as senior representatives from shipowners, energy majors, bunker operators, port authorities, class societies and technology suppliers explored how to strengthen the framework for clean fuels in shipping.
The socially distanced edition of Gas Fest, now in its 4th year and hosted for the first time by SGMF, comprised interactive online sessions across five areas: infrastructure, design and technology, alternative fuels, communications and defining sustainability. The workshops also featured live graphic facilitation to capture the discussions, a hallmark of Gas Fest since its inception.
“Gas Fest has always delivered honest discussions and real action,” said Mark Bell, General Manager, SGMF. “Although we could not meet physically this year, the virtual workshops showed that the community built around the event remains energised and committed to clearing a smooth and safe path for the increasing uptake of LNG and, as they become viable, other fuels that can contribute to cleaner shipping.”
Debunk(er)ing the myths
In the opening session, participants explored some of the perceptions of LNG as a marine fuel. Comparisons of clean fuel candidates can give the impression that fuels such as green hydrogen, methanol and ammonia are close to commercial availability. In fact they are many years away and LNG is an important first step, offering clear emission advantages today as well as potential for future greenhouse gas emission reductions, either by synthetic methane or bio-LNG – which can be used as drop-in fuels to gradually lower emissions – or to other cryogenic clean fuels.
Shipowners require long-term certainty and the idea of a ‘bridge’ fuel may encourage them to look to future solutions that are not yet ready. Describing LNG instead as an ‘incremental’ fuel that can be gradually made cleaner over the lifecycle of a vessel may provide reassurance that owners’ technology investments will not be stranded.
Infrastructure investment
A similar message could help stimulate the investment in infrastructure needed to enable more widespread use of LNG as marine fuel. A separate session found that perceived uncertainty of returns was holding investors back, with few governments giving clear signals about the long-term future of LNG and few companies prepared to take risks to develop bunkering markets without these cues. This investment is needed to drive infrastructure to the stage where it is capable of serving vessels trading on the spot market, which have no fixed schedule and can only bunker where they are sent.
The infrastructure session also took a deep look at the current state of LNG bunkering. Reducing the cost of LNG bunker vessels was seen as key to encouraging uptake, with designers considering how the next generation of vessels could be made more cost-effective. At the same time, it was agreed that a wider range of bunker vessel sizes will be needed to ensure all vessel sizes are served.
Future fuel ready
The incremental advance towards carbon-neutral fuels is also being noted by technology designers, as described by participants in the alternative fuels sessions. Many are already being asked for concepts that are ‘future fuel ready’ even though some characteristics of these fuels – their emissions on combustion, for example – remain relatively unknown. That pressure represents a ‘palpable change’ over the past year or so in the approach shipowners are taking to investigating future fuel options.
While the pace of investigation is accelerating, shipowners have yet to narrow down the direction of change. Participants revealed that owners are reluctant to eliminate fuel candidates prematurely because of the grave risk of making a wrong decision. Another reason is that shipping may have only a limited influence in which fuels it eventually has access to, with competition for clean fuels coming from national grids and other, bigger, industries. In this context, flexibility, preparedness and willingness to deploy new fuels and technologies is more important than predicting which fuels will be available.
The uncertainty of the future fuel outlook again highlights the challenge for LNG’s label as a ‘bridging’ fuel. While clean fuels of the future – i.e. the ‘end of the bridge’ – are not clear, LNG offers immediate emission advantages today and the potential to incrementally improve environmental impact.
Next steps
The Gas Fest community, comprising around 150 targeted participants representing over 50 organisations, across the gas as marine fuel value chain, are committed to regular virtual meetings whilst hoping for an in-person meeting in July 2021 in Barcelona.
Gas Fest is a unique ‘for industry, by industry’ platform that convenes key players across the fuel value system to explore the role of gas as a marine fuel in shipping’s energy transition. Since the first gathering in 2017 it has been an essential collaborative forum for identifying concrete steps to advance the decarbonisation of the marine industry through the use of gas as a marine fuel. From 2020, Gas Fest is hosted by the Society for Gas as a Marine Fuel (SGMF) and key industry partners.
About SGMF:
The Society for Gas as a Marine Fuel (SGMF) is a non-governmental organisation (NGO) established to promote safety and industry best practice in the use of gas as a marine fuel. It has Consultative Status with the IMO and is the definitive information resource for the industry.
Formed in 2013, Governed by a representative Board, the Society is driven by two principal Committees; Technical and Environmental. SGMF has several Working Groups at any one-time solving issues and producing outputs such as Formal Publications and Technical Guidance Notices for the industry. The Society has produced s number of ISBN publications to date and has over 148 international members ranging including energy suppliers, port authorities, fuel suppliers through to equipment manufacturers, training organisations and classification societies. SGMF are a consulting member of the IMO, and work in collaboration with a range international shipping and ports NGOs.
SGMF’s members currently sits at 148 members as of June 2020. To view the full list member organisations can be found at: www.sgmf.info/profiles/search