Innovative Knowledge Transfer Partnership blade project achieves important milestone in move to shorter and more cost effective blade tests.
A project to develop a new bi-axial blade fatigue testing method – aimed at reducing fatigue test times by almost a half and overall test times by a quarter – has achieved an important milestone after the software being developed by the Offshore Renewable Energy (ORE) Catapult received certification from DNV GL, the world’s largest resource of independent energy experts and certification body.
The two year collaborative Knowledge Transfer Partnership project between ORE Catapult and Durham University, which was partly funded by Innovate UK, is developing a method to optimise the design of fatigue tests – which are used to demonstrate that a blade can survive its design lifetime – and enable bi-axial blade testing.
Certification of the ORE Catapult software by DNV GL provides vital assurance to clients that the results the new test method will generate will conform to industry standards and guidelines. This paves the way for the next phase of the project, which is to use the software to demonstrate a bi-axial test at full scale using the Catapult’s blade test facility in Blyth, Northumberland.
It is hoped this real-life test will show that an optimised bi-axial test – flapwise and edgewise fatigue testing being carried out simultaneously – offers very significant time benefits when compared to single axis testing thanks to an accurate estimation of the induced blade damages, leading to reduced costs as well as improving how representative the test is of the blade loading seen in service.
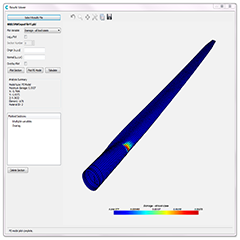
The new process involves blade geometry, materials and loading data being input into the software, which then performs a fatigue analysis on the blade. The output from this software can then be used to design a fatigue test for the customer. All the necessary blade testing information is then held in a single file, significantly simplifying the traditional fatigue testing process and leading to shorter test times and reduced costs.
Peter Greaves, Research Structural Engineer – Blades, commented: “It’s great that we’re now getting into the final stages of developing this method as an ORE Catapult testing product, and getting the fatigue analysis software certified by DNV GL is a key part of that. The bi-axial blade fatigue testing software allows us to gather all of the information that we need in order to design a blade test in a fraction of the time that it currently takes, whilst giving the customer confidence that the results conform to the relevant standards.”
Ignacio Marti, Innovation & Research Director, commented: “This is a significant development for ORE Catapult. It highlights and strengthens the importance and impact that research and innovation can have on better informing and improving our test programmes, which in turn has a positive impact on the client and the wider offshore renewable energy industry.”
Single axis vs bi-axial fatigue testing
The purpose of the fatigue test is to demonstrate that the blade can survive its design lifetime. The loads are increased to accelerate the test, which is performed using a hydraulic excitation system to resonate the blade at its natural frequency for a few million cycles in the flapwise direction and then the edgewise direction. During operation the blade is loaded in both the flapwise direction (out of the rotor plane) by aerodynamic forces and in the edgewise direction (in the plane of the rotor) by gravity as the rotor spins. Single axis fatigue testing treats these sources of loading separately so it is less realistic. Bi-axial fatigue testing means that both blade axes are fatigue tested at the same time, meaning the blade moves both up-and-down and side-to-side during the test.
About the Offshore Renewable Energy Catapult
ORE Catapult was established in 2013 by the UK Government and is one of seven such Catapults set up by Innovate UK in high growth industries. It is the UK’s flagship technology innovation and research centre for offshore wind, wave and tidal energy.
ORE Catapult delivers prioritised research underpinned by world-class test and demonstration facilities, collaborating with industry, academia and Government to reduce the cost of offshore renewable energy and create UK economic benefit.
The economic opportunity for the UK is immense, with the potential for huge employment, GVA and exports of technology, skills and services, potentially mirroring the success of the oil and gas sector over the past thirty years.
The Catapult programme represents a £1.4bn funding commitment from the public and private sector over five years. Long term, the Catapult will be funded 1:1:1 by central government, the private sector and other sources of funding such as the EU and devolved Governments.
DNV GL in the Energy industry
In DNV GL we unite the strengths of DNV, KEMA, Garrad Hassan, and GL Renewables Certification. DNV GL’s 2,500 energy experts support customers around the globe in delivering a safe, reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy supply. We deliver world-renowned testing, certification and advisory services to the energy value chain including renewables and energy efficiency. Our expertise spans onshore and offshore wind power, solar, conventional generation, transmission and distribution, smart grids, and sustainable energy use, as well as energy markets and regulations. Our testing, certification and advisory services are delivered independent from each other. Learn more at www.dnvgl.com/energy