Accurate measurements of broadband solar irradiance require radiometers with proper design and performance characteristics, correct installation, and documented operation and maintenance procedures, including regular calibration. With any measuring tool, calibrations must be traceable to a recognized reference standard. For direct normal irradiance (DNI) measurements of broadband solar radiation, the World Radiometric Reference (WRR) is the internationally recognized measurement standard.
The WRR was established by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1977 and has been maintained by the Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium Davos, World Radiation Center (PMOD/WRC) in Switzerland. The center maintains a group of five cavities as part of world primary reference standard.
The ACR model HF manufactured by The Eppley Laboratory has been one such reference standard-level device since 1978.
Field pyranometers and pyrheliometers must be calibrated against more accurate pyrheliometers with clear WRR traceability. The most accurate pyrheliometers are electrically self-calibrating absolute cavity radiometers (ACR). These are typically not deployed in the field as they are an order of magnitude more expensive than regular pyrheliometers and are often used without any optical windows.
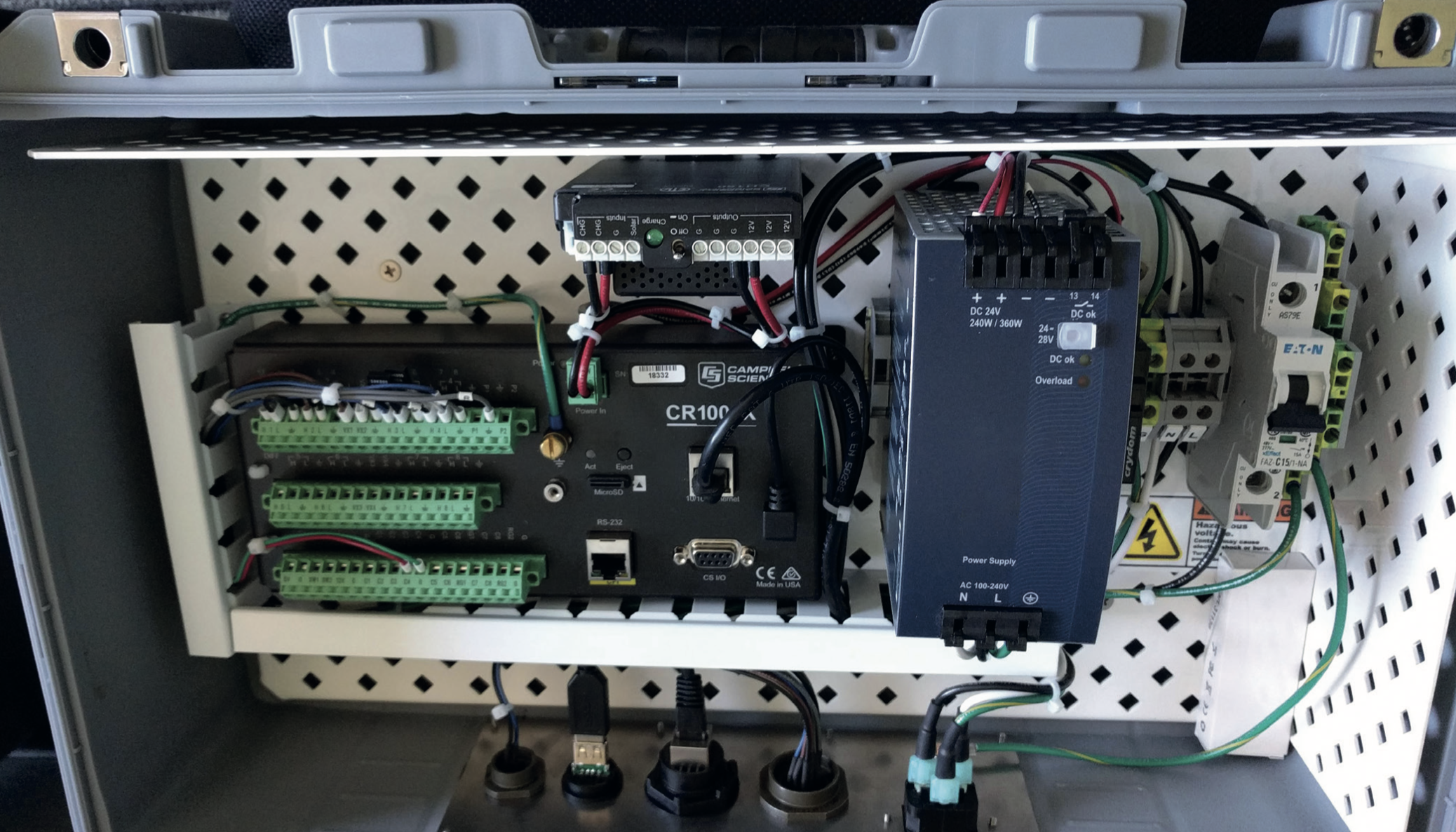
ACRs require a controller unit to make periodic self-calibrations and solar radiation measurements. Signals produced are very small and high-accuracy levels are desired. Traditionally, high end laboratory equipment is used for this application. Campbell Scientific’s newer data loggers, the CR6 and CR1000X, have the desired accuracy levels and are field deployable.