The recycling of wind turbine rotor blades represents a major challenge within the energy transition. The recycling of other turbine components, such as towers made of steel and concrete, foundations and nacelles with integrated electronic components, is generally relatively uncomplicated. The complex material composition and structure of rotor blades mean that recycling them requires considerable technical and economic effort. For this reason, work is underway in a variety of research projects at the Fraunhofer Institute for Wind Energy Systems IWES to develop systematic approaches to address this challenge.
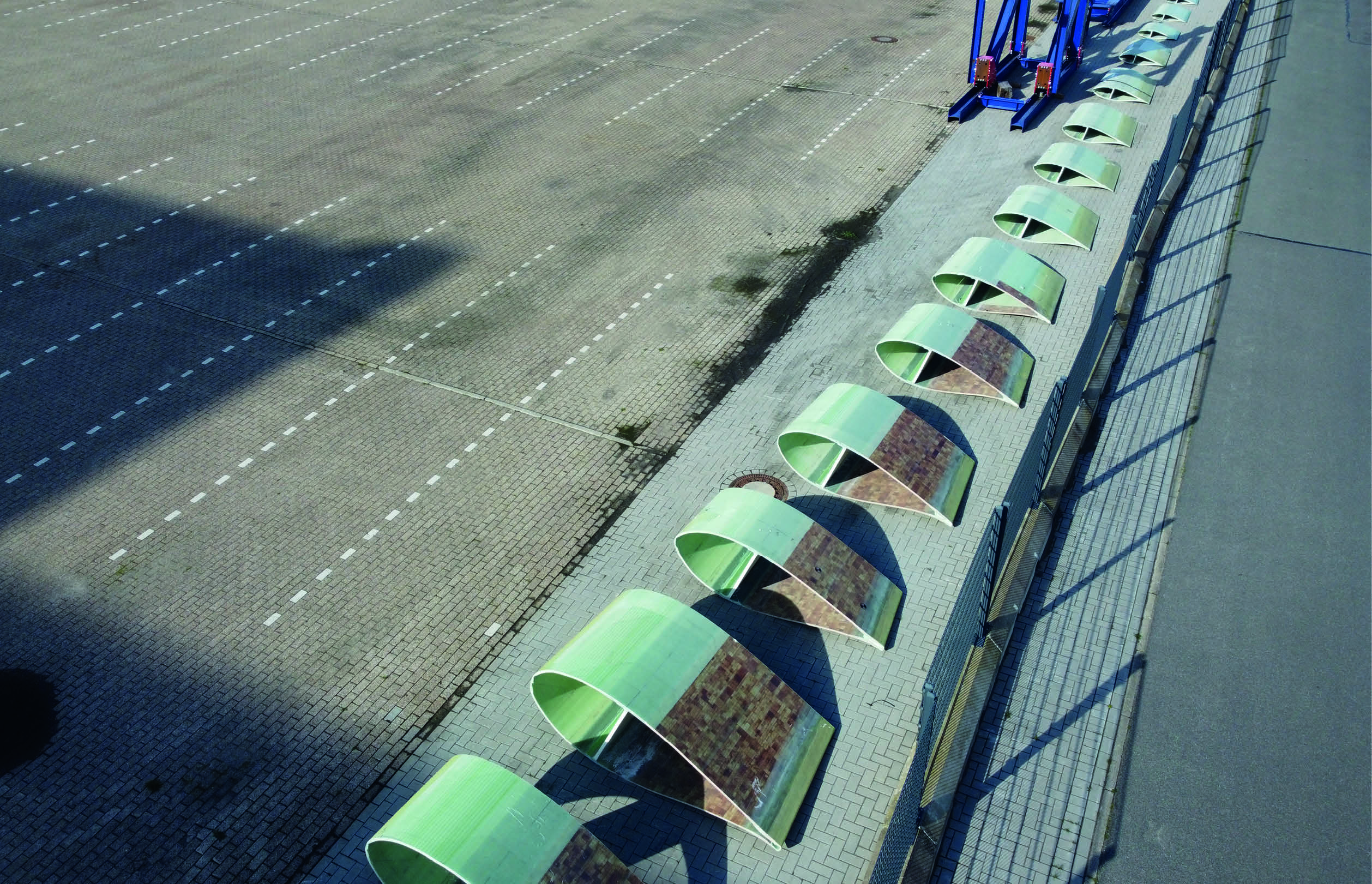
Material complexity of rotor blades
Rotor blades are predominantly composed of glass fiber-reinforced and carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (GFRP and CFRP), which, in combination with other materials, produce a robust and functional overall design. These specific materials are preferred in the wind energy sector because of their excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength while still being lightweight.
Rotor blades are typically designed as a sandwich construction or full-laminate structure, using fibers, balsa wood and PET or PVC foam embedded in a thermoset matrix. This diversity of materials increases the requirements for effective separation, which is necessary for the recycling of the individual components to guarantee a high-quality recycling solution.
Download full article